Wikijunior:Biology/Tissues
Tissues edit
Organisms are made of tissues. Tissues are groups of cells that work together. Plant leaves have tissues that capture light and make sugar. Most animals have muscle tissues that help them move.
When two or more tissues work together to do one thing, they make up organs.
In most Animals, there are four types of tissues:
- Epithelial tissue: This forms the borders of organs, and lines cavities or surfaces.
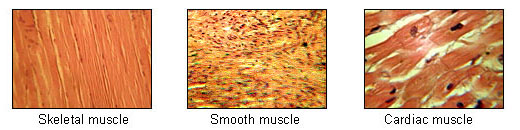
- Muscle tissue: Moves the body.
- Nervous tissue: Sends signals throughout the body and forms the brain and sense organs.
- Connective tissue: Holds the body together. It includes the blood, bones, and fat.
In plants, there are two types of tissues:
- Meristematic tissue: This has actively dividing cells.
- Permanent tissue: This type of tissue has developed cells. They do not divide.
There are also two different types of permanent tissue:
- Simple permanent tissue: This type of permanent tissue has only one kind of cells. Some examples of simple permanent tissues are:
- Parenchyma: They have loosely packed cells. The cells do not have a particular function.
- Collenchyma: They have cells which have layers called pectin. They contain chlorophyll.
- Sclerenchyma: They have dead cells. Between the cells, there are layers called lignin.
- Complex permanent tissue: This type of permanent tissue contains different kinds of cells. Some examples of complex permanent tissues are:
- Xylem: This type of tissue contains mainly dead cells. They help to move water from the roots to leaves.
- Phloem: This type of tissue contains mainly living cells. They help moving food materials from leaves to other parts.