The Organ Systems/circulatory
The Circulatory System
Function of System:
Circulates blood, nutrients, hormones, oxygen, and other substances throughout the body.
How it aids in homeostasis:
Helps to fight diseases, maintains internal body temperature, and maintains proper pH.
Image of system:
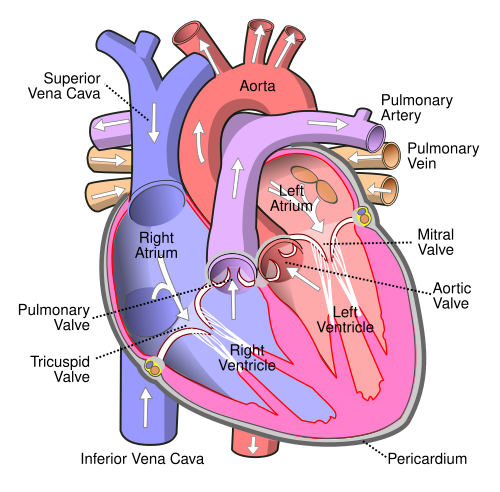
Major Organs:
Heart - Pumps the blood throughout the body. Arteries - Carry blood away from the heart. Veins - Carries blood toward the heart. Blood - Contains hemoglobin which aids in oxygen transport.
Human Heart: Four chambers
Comparative Anatomy:
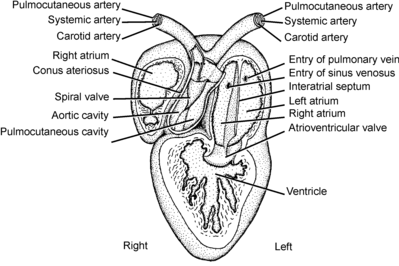
Human hearts have four chambers. Frogs have three chambers. The fish heart only has an atrium and a ventricle. Blood is transported from the heart to the Arteries through Arterioles and then to the capillaries, it comes back to the heart through venules and then to veins. All three organisms have closed circulatory systems.
Fish: Two chamber heart
Frog: Three chamber heart
Diseases of the Circulatory System:
Cardiomyopathy is a disease of the circulatory system. The name cardiomyopathy when broken down means diseased heart muscle; cardio (heart), myo (muscle), and pathy (disease). Disease happens when one or both of those chamber and pump systems are not functioning properly. There are three main ways the chambers can be damaged and that cause cardiomyopathy. The three areas are a "power failure, small pump, and a blocked pump" (McPheeters, 2014).

In dilated cardiomyopathy the picture shows how the chamber swells up affecting the flow of blood leaving the heart. In the hypertrophic heart it shows the chamber that shrank which results in less blood flowing through.
Cardiomyopathy disrupts homeostasis in the body through blood pressure abnormalities. This disease affects the heart's abilities to pump blood efficiently in the body, with that disruption blood is pumped slower which affects the patients blood pressure levels. The blood pressure levels decline, homeostasis in the body tries to regulate the drop in blood pressure. Homeostasis in the body is effected by red blood cell imbalance, vessel dysfunction and vasoconstrictors.
In Animals
Dilated Cardiomyopathy affects dogs in particular as far as comparative anatomy. It is a genetic disease so it is passed on through the parents. The disease affects larger breeds of dogs and rarely affects smaller breeds. Cardiomyopathy is a treatable disease and the earlier a dog is diagnosed with any form of heart disease the prognosis is better (Llera & Ward, n.d.).
Reference sources (APA):
Esi.stanford.edu. N.p., n.d. Web. 12 Apr. 2017. " Ribbiting Facts on the Human and Frog Circulatory and Respiratory Systems." Emaze Presentations. N.p., n.d. Web. 12 Apr. 2017.
Llera R., & Ward E. (n.d.). Dilated Cardiomyopathy in Dogs. VCA Animal Hospitals. Retrieved April 12, 2023 from http://vcahospitals.com/know-your-pet/dilated-cardiomyopathy-dcm-in-dogs--indepth
McPheeters, M. (2014, September 12). Cardiomyopathy signs and symptoms. Circulatory System and Disease. NCLEX-RN. Khan Academy. YouTube. Retrieved April 12, 2023, from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iL6aM2xFixU
Return to Table of Contents